how do packet delay and loss occur ?
: the time when the router's switch buffer is full
-transmission delay ? the time it takes for a packet to go out over the link
-queueing delay ? the sum of transmission delays in front of packet
ex) transmission delay = 1sec , the 100th's queueing delay ?
=> the sum of transmission delays in front of 99th packets
packet delay : four elements
dtotal nodal = dproc + dqueue + dtrans + dprop
dproc : nodal processing delay
-> the time for making a decision on packet forwarding
-> chack the bit error
-> decision of output link
-> nanosec scail
dqueue : queueing delay
-> buffer waiting time before transmission
dtrans: transmission delay
->L(packet length)/R(link transmission rate)
->the time it takes to exit the switch
propagation delay :
-> varies with the medium ex) fiber cable
-> more cable length results in more delay ex) korea -> usa
packet queueing delay (revisited)
a : the average of packet arrival rate
L : the packet length
R : link bandwidth
L * a/R : arrival rate of bit / service rate
* both are fixed but queueing delay continuously changes
-> the remainder are also fixed
ex) ticketng
- the packet buffer size is small regardless of switch memory size
- if it is large , the queueing delay is infinite
- so to prevention, it is intentionally limited to a small size
packet loss
-> during the packet handling , the packet is stored in memory .
if it is copied , the packet enters the queu otherwise it is droped.
-> the packet is coverd by the next received packet
-> conclusion : the memory copy state
throughput
= how much packets can transmitted per sec
(between sender and reciever)
* because of the varying queueing delay experienced by packet at each moment, the throughtput also fluctuates
* the low delay -> heigh throughput
*ping : measure the latency
*everage throughput ? limited by the minimum throughput
throughput : network scenario

->the bottleneck is where the bandwidth is smalleast
* the core net dosent create a bottleneck
why layering?
-obvious structure creates unity
-implementing modularity makes maintenance more convenient
ios/osi network class

layered internet protocol stack
application : supporting network applications ex) http,dns,smtp
transport : process-process data transfer ex)tcp,udp
network : routing of datagrams from source to dest ex)ip,routing protocols
link : data transfer between neighboring network elements ex) ethernet, wifi
physical : bits on the wire
services, Layering and encapsulation
- the message is delivered by being processed into a packet
- the packet is encapsulaized by passing through each layer, attacheing header
- the destination unpacks the packet in reverse order
* the network is stratified -> each layer has its own role
* but the layered architecture incurs overhead
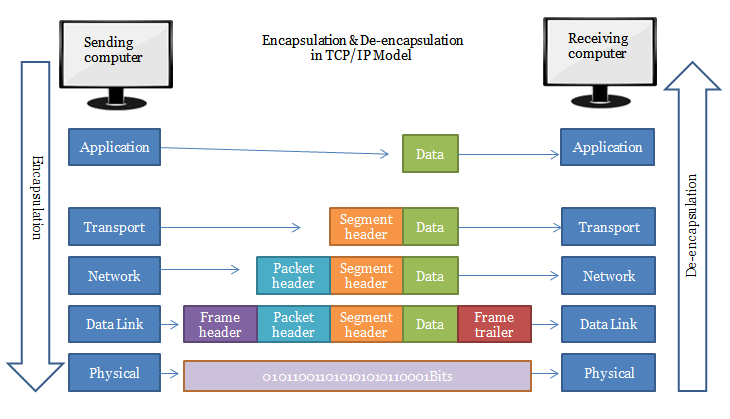
* each layer calls paket in a different way
'cs > computer Networks' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Network core (2) | 2023.12.31 |
|---|---|
| computer Network big picture (0) | 2023.12.30 |
